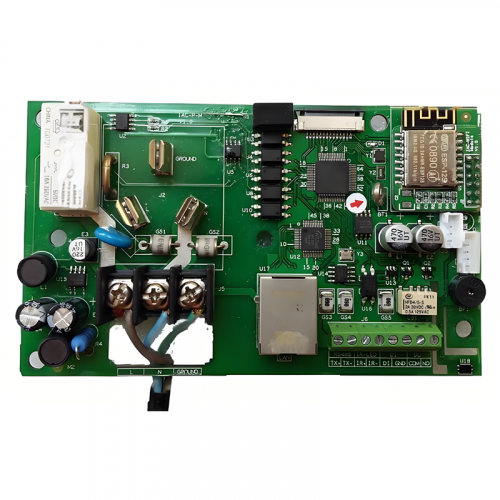
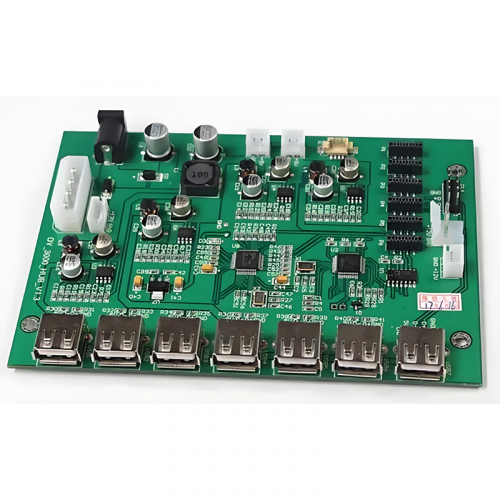
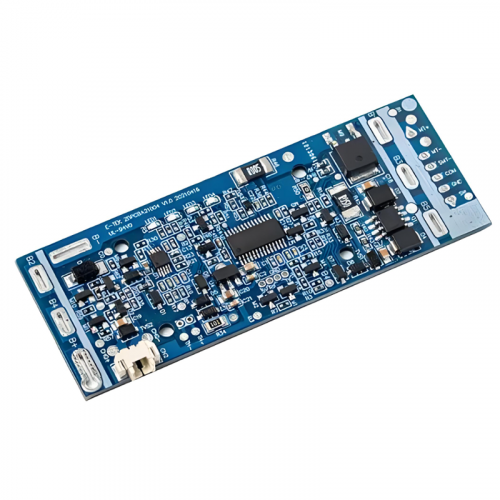
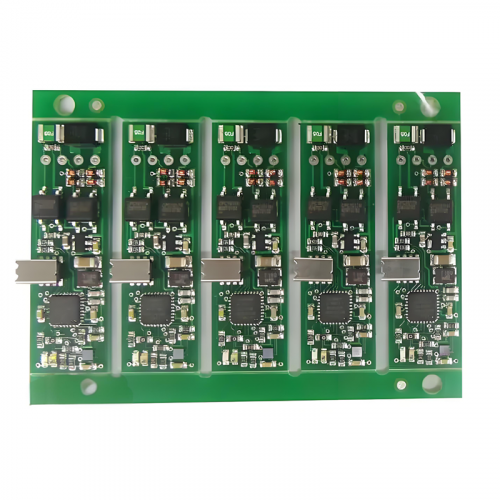
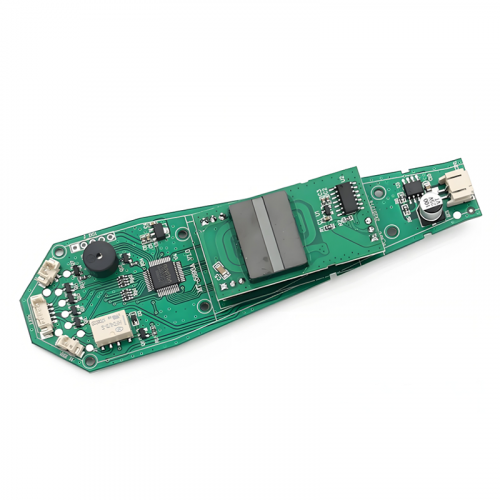
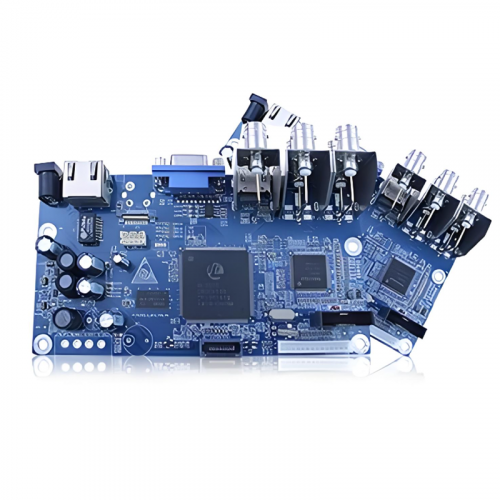
The PCBA process involves several intricate steps to ensure high-quality assembly. Initially, the PCB is prepared with conductive traces, pads, and vias to create pathways for electricity. Components are then mounted onto the PCB using either Surface Mount Technology (SMT) or Through-Hole Technology (THT), depending on the design and application. SMT involves placing components directly onto the PCB surface, whereas THT requires inserting component leads through drilled holes. Advanced techniques like wave soldering, reflow soldering, and manual soldering are employed to secure the components. Quality assurance processes, such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection, are essential to detect and rectify assembly defects.